Are you a Health Coach supporting clients to make healthy lifestyle changes?
Each day, you’re navigating the complex nature of behaviour change.
You might have heard of The Transtheoretical Model (TTM), also known as the Stages of Change Model, a psychological framework developed by Prochaska and DiClemente in the 1980s.
The TTM outlines a series of stages we go through as we work to change our behaviour:
- Precontemplation – not yet considering change.
- Contemplation – considering change but haven’t committed to taking action.
- Preparation – making a commitment to change and taking the initial steps.
- Action – taking significant action to change our behaviour.
- Maintenance – successfully changing our behaviour.
Many people initiate coaching during the contemplation stage. As a coach, it’s your job to guide someone to the maintenance phase – often through the loss of the old and the anxiety of something new.
Although this model gives some reasonable guidance regarding how to change behaviour, others have argued that it doesn’t provide a particularly complete or accurate description of behaviour change.
So, what other theories are available that you may find useful?
In this article, we’ll explore the COM-B Model.
The COM-B Model
Susan Michie, Maartje M van Stralen, and Robert West developed the COM-B model in 2011 after analysing 19 existing frameworks for behaviour change.
Whereas the TTM focuses on the process of change, the COM-B model focuses on the factors that influence behaviour change.
The TTM is the how of change, and the COM-B Model is the why.
So, what makes people change? The COM-B model categorizes three key influences: Capability, Opportunity, and Motivation.
- Capability – the individual's ability to perform a specific behaviour.
- Opportunity – the properties of the person’s environment that provide opportunities to conduct the behaviour.
- Motivation – the individual's psychological process that energises and directs the behaviour.
These key influences are further broken down into two categories each.
Capability Influences |
Opportunity Influences |
Motivation Influences |
|
Physical Does their body allow them to change behaviour?
Psychological Does their mind allow them to change behaviour?
|
Social How does their social environment affect their opportunity to change?
Physical How does their physical environment (i.e., their surroundings, time and material resources) affect their opportunity to change?
|
Automatic Do their habits and emotions drive them towards change?
Reflective Do their beliefs and plans drive them towards change?
|
In the COM-B Model, both capability and opportunity can influence and interact with motivation, either enhancing or hindering it.
For example, if someone has the physical capability to prepare healthy meals and understands how to do it, they may feel more confident about making healthier food choices, which, in turn, can boost their motivation to engage in healthy eating.
Here’s an overview of the model:
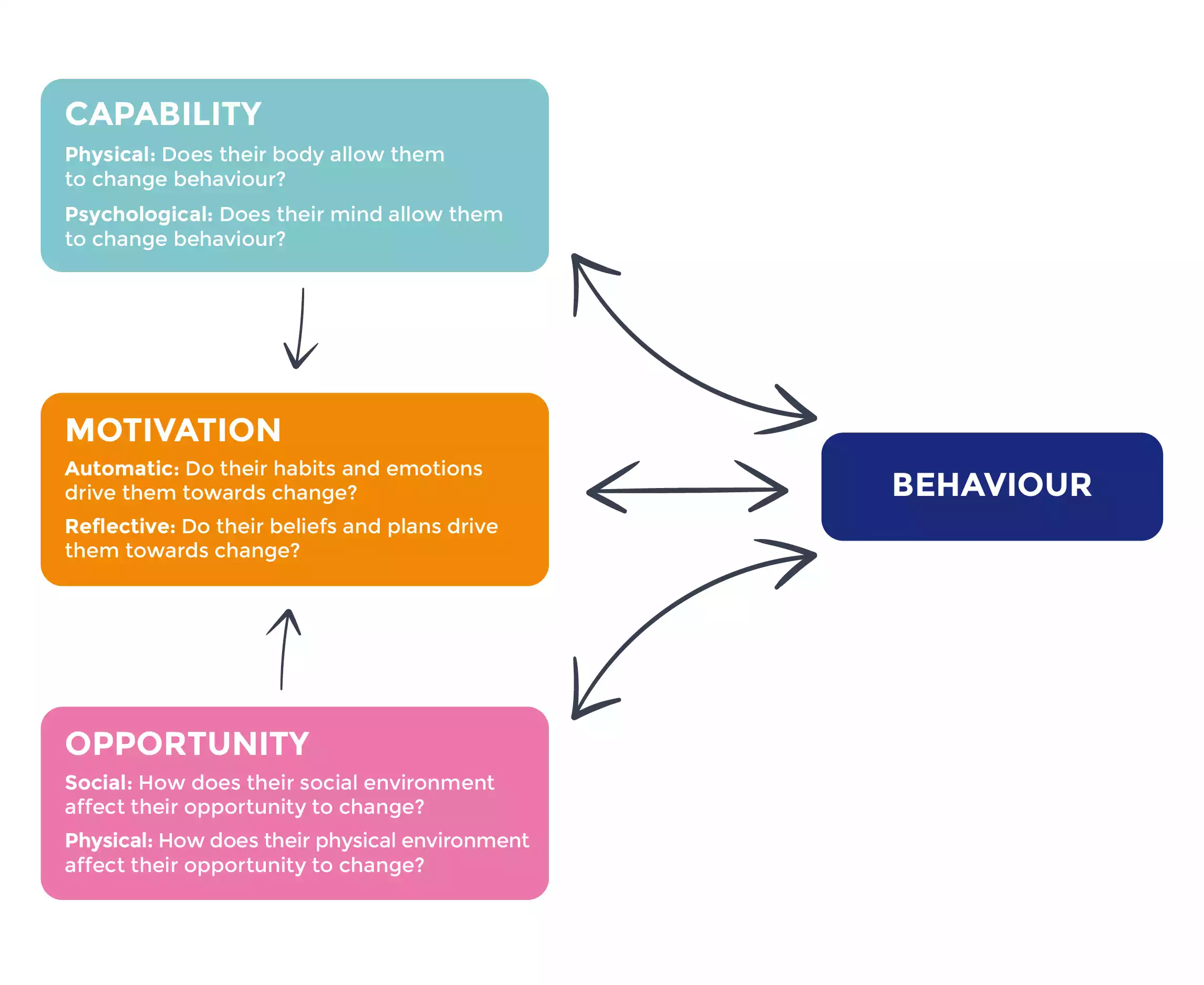
The COM-B Model in Practice
The COM-B Model can be applied to a wide range of contexts, including coaching.
For example, the NHS’s Workforce development framework for health and wellbeing coaches specifies that coaches must be able to:
"Explores the risks, benefits, and consequences of different courses of action with the client. Discusses what these mean to the person in the context of their life and goals, supporting them to be able make a decision and/or agree the way forward together (for example, in context of COM-B model etc)"
Along with the TTM, the COM-B model is the most commonly used model of behaviour change in the NHS.
So, how can you begin to use this model in your coaching practice?
Let’s start with an example.
Your client, Linda, wants to reverse her diabetes type 2 diagnosis by focusing on improving her diet. She works long hours and usually gets takeaway food on the way home from work.
Conducting a COM-B Diagnosis
- Capability influences – Does she know what she should be eating (psychological)? Is she physically able to cook (physical)?
- Opportunity influences – Does she have people in her social circle that will support her to change her diet (social)? Does she have adequate cooking equipment (physical)?
- Motivational influences – Does she unconsciously reach for unhealthy snacks when stressed (automatic)? Does she have a clear plan about what she will eat (reflective)?
The model states that if any of these influences aren’t sufficiently addressed, Linda will not change her diet.
According to the model, making real and lasting changes in behaviour means you've got to enhance at least one key influence: capability, opportunity or motivation.
Example Coaching Questions Using the COM-B Model
Capability Enhancement Questions
- "Linda, what do you currently know about a diabetes-friendly diet, and are there any areas where you'd like to learn more?"
- "Are there any barriers or challenges you face when it comes to preparing meals at home?"
Opportunity Enhancement Questions
- "Who in your social circle can support you in making dietary changes? Do your friends or family have any dietary preferences that might affect your food choices?"
- "Do you have all the necessary cooking equipment to prepare healthier meals at home, or is there something you need to buy?"
Motivation Enhancement Questions
- "What are the primary benefits you see in changing your diet to manage your diabetes better? And what, if any, concerns do you have about making these changes?"
- "Do you have a clear plan in mind for what you'll eat, and have you considered how to integrate these changes into your daily routine?"
Once you've identified which components are mostly affecting the client’s behaviour, you can work with them to develop the appropriate intervention strategies.
Remember, sustainable behaviour change takes time, and it's essential to help clients set realistic expectations, work on habit formation, and develop resilience in the face of setbacks.
Summary
The COM-B model simplifies behaviour change by pinpointing the essential factors required for a behaviour to occur: capability, opportunity and motivation.
The COM-B model equips coaches with a systematic and comprehensive framework for guiding their clients toward successful behaviour change, whether it's related to health, lifestyle, or personal development.
Think this framework could be helpful in your coaching practice? Click to download our free COM-B Diagnosis Worksheet below.
Build Your Coaching Toolkit
Want a library of practical tools to share with clients? Check out The Professional's Mental Wellbeing Toolkit today. It's "everything you need all in one place."





